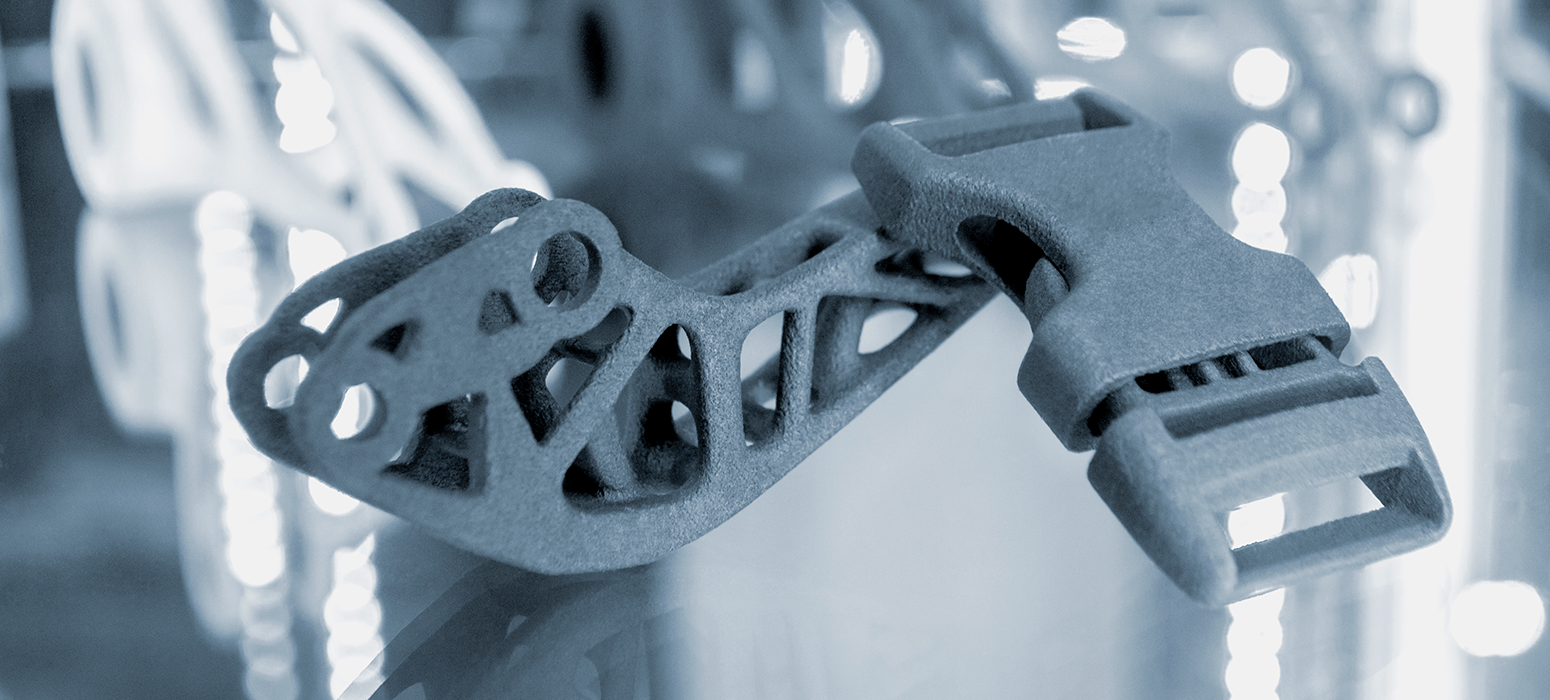
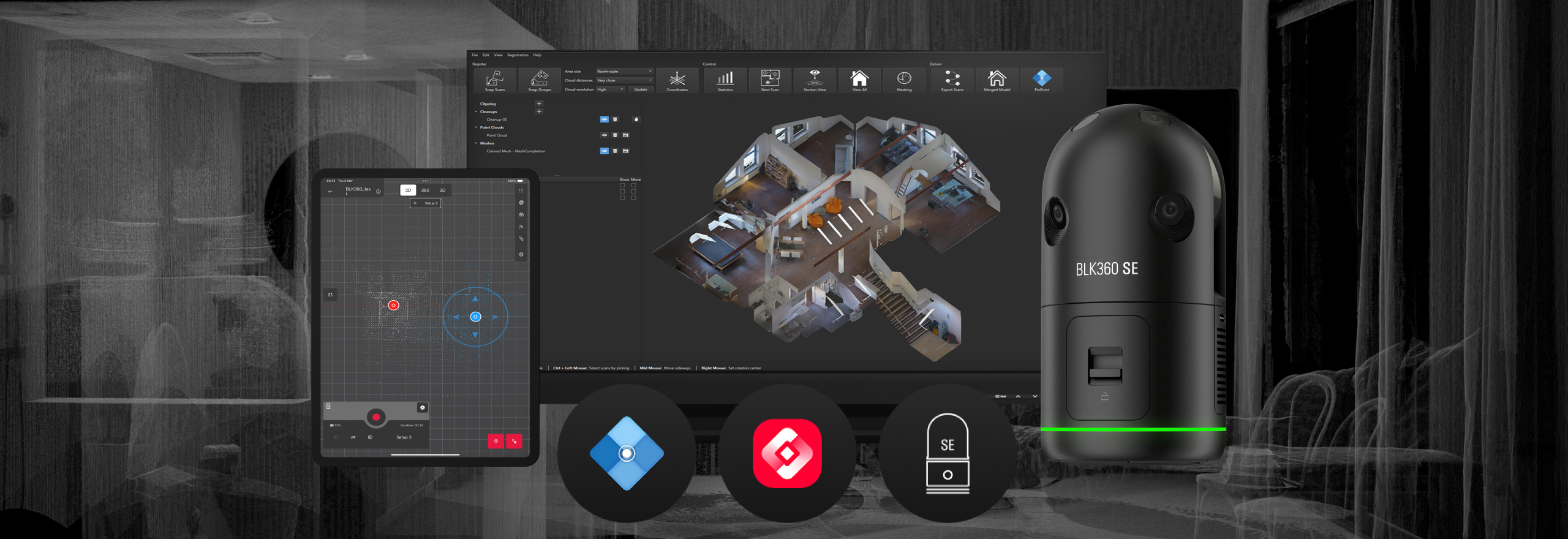
Why Scan-to-CAD Is Essential
In many engineering and manufacturing scenarios, original CAD data is unavailable, outdated, or no longer accurate. Scan-to-CAD, commonly referred to as reverse engineering, provides a reliable solution by converting physical objects into precise, editable CAD models. This process bridges the gap between existing physical parts and modern digital workflows, enabling redesign, inspection, and manufacturing with confidence.
Instead of forcing conventional design rules onto additive processes, DfAM uses the strengths of additive manufacturing from the beginning. Engineers take advantage of geometric freedom, internal features, and optimized material placement. This approach allows the creation of parts that are lighter, stronger, and more functional while reducing material waste, minimizing post processing, and eliminating unnecessary assembly steps.
When Original CAD Data Is Missing or Incomplete
Many legacy or in-service components were manufactured before digital design processes became standard. In other cases, CAD files may be lost, corrupted, or unavailable due to supplier changes. This is especially valuable for:
- Legacy and discontinued parts
- Supplier-dependent components
- Maintenance and repair operations

Design Modification and Optimization
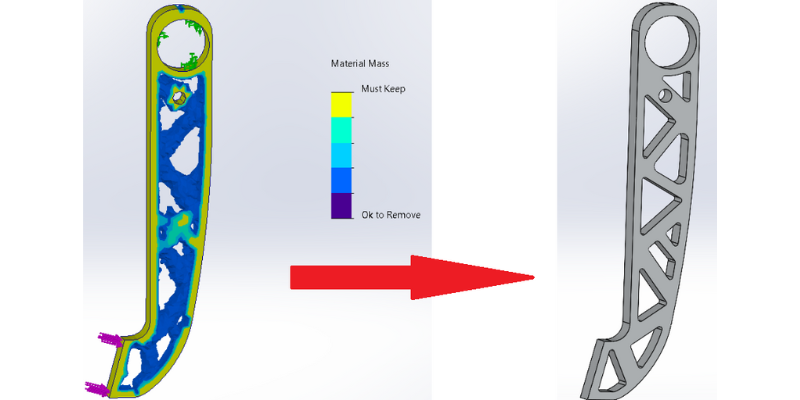
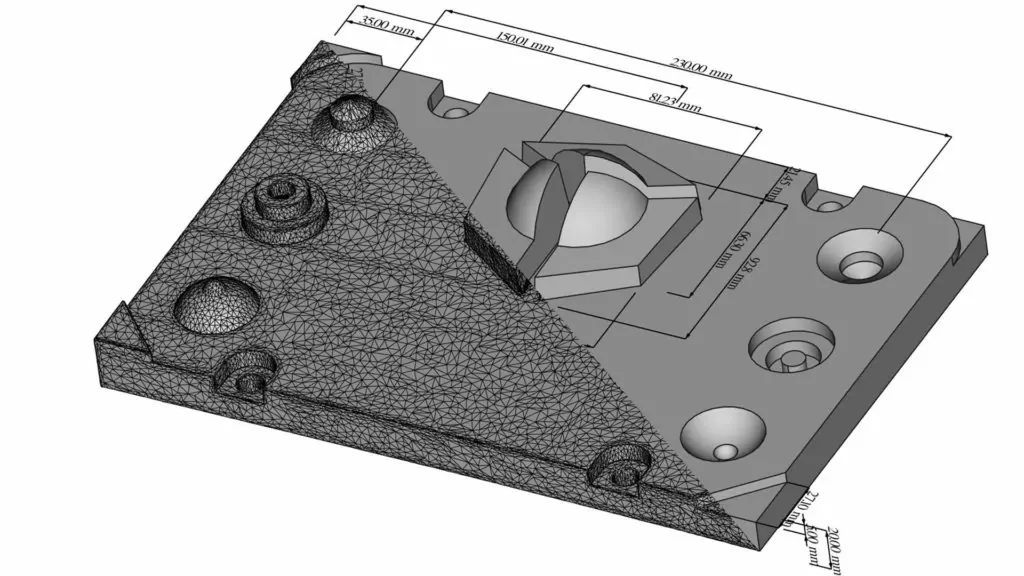
Scan-to-CAD is not limited to copying existing parts. Once scan data is converted into a parametric CAD model, engineers can modify geometry to improve performance, reduce weight, or enhance manufacturability. Common use cases include:
- Improving part strength or durability
- Adapting parts for additive manufacturing
- Updating designs to meet new requirements
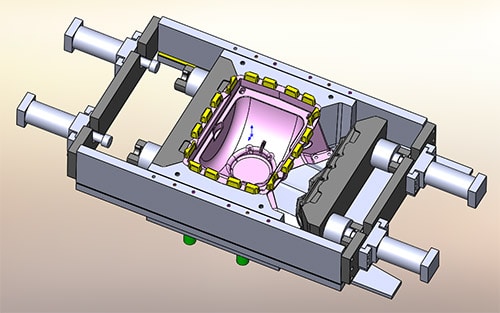
Tooling, Molds, and Fixture Updates
Accurate CAD data is essential for modifying tooling, molds, dies, and fixtures. Scan-to-CAD enables precise measurement and reconstruction of existing tooling, allowing engineers to update or repair tools without relying on original drawings. Benefits include:
- Faster tooling redesign
- Reduced downtime
- Improved fit and alignment
Quality Inspection and Deviation Analysis
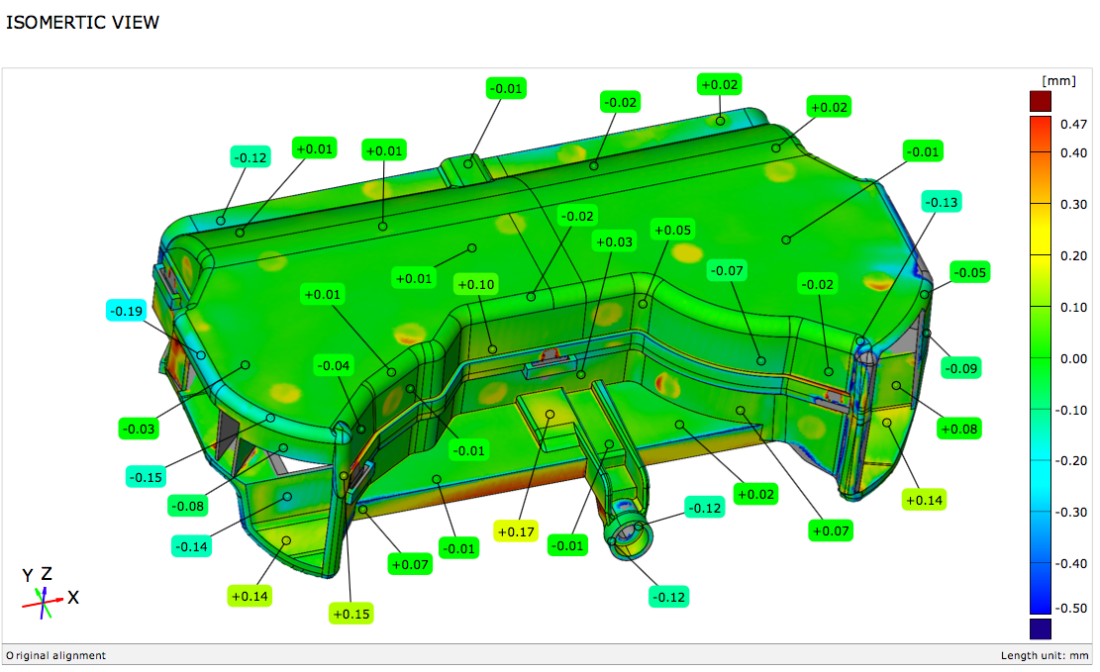
Reverse-engineered CAD models can be used to compare manufactured parts against design intent. By aligning scanned data with CAD geometry, engineers can perform deviation analysis to identify dimensional inaccuracies, wear, or deformation.
This supports:
- Quality control and inspection
- Wear and damage assessment
- Process validation
Scan-to-CAD is essential whenever physical parts need to be digitized, modified, inspected, or reproduced accurately. By converting real-world geometry into precise CAD models, reverse engineering reduces downtime, improves design flexibility, and supports smarter manufacturing decisions. It is a vital capability for industries that depend on accuracy, efficiency, and reliability.