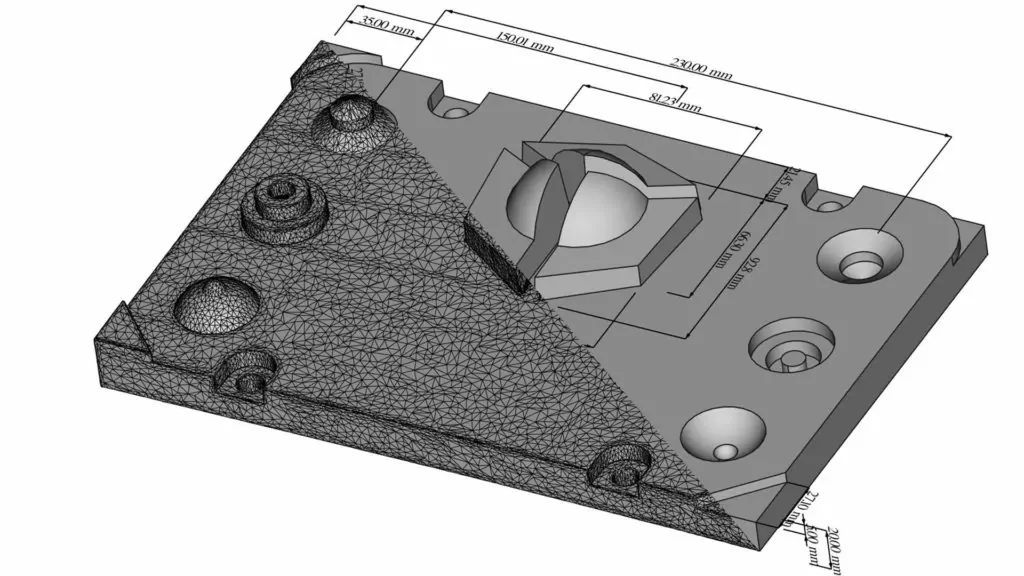
3D Scanning Applications Across Industries
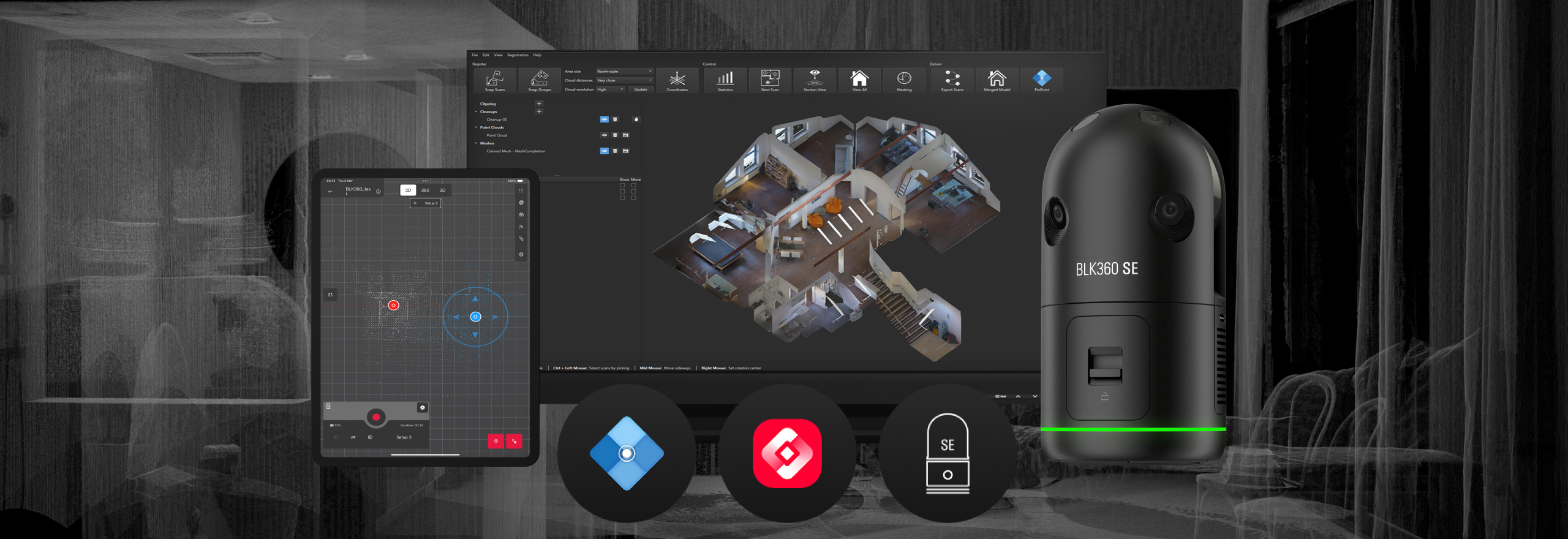
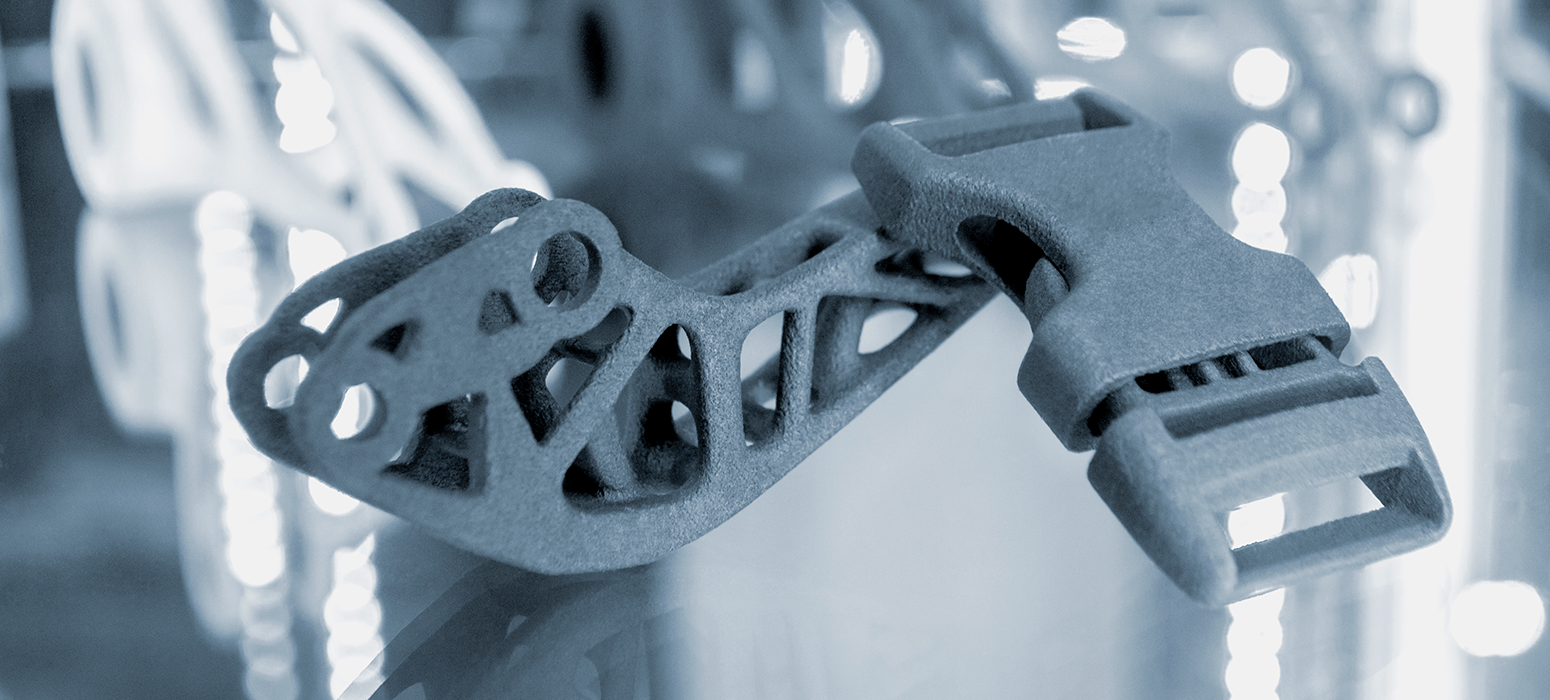
3D scanning has become an indispensable technology in modern engineering, manufacturing, and digital transformation. By capturing the precise geometry of physical objects and environments, 3D scanning converts real-world surfaces into highly accurate digital models. These models enable organizations to design better products, inspect components with confidence, and make faster, data-driven manufacturing decisions.
Unlike traditional measurement techniques, 3D scanning captures millions of data points in seconds, ensuring accuracy even for complex shapes, free-form surfaces, and hard-to-reach areas. As a result, industries that demand precision, speed, and repeatability increasingly rely on 3D scanning as a core part of their workflows.
Must explain to you how all this mistaken idea of denouncing pleasure and praising pain was born and I will give you a complete account of the system, and expound the actual teachings of the great explorer of the truth, the master-builder of human happiness. No one rejects, dislikes, or avoids pleasure itself, because it is pleasure, but because those who do not know how to pursue pleasure rationally encounter consequences that are extremely painful. Nor again is there anyone who loves or pursues or desires to obtain pain of itself, because it is pain, but because, occasionally, circumstances.
Key Industry Applications of 3D Scanning
1. Manufacturing & Quality Control
- Reduce scrap and rework
- Improve production consistency
- Shorten inspection times
- Ensure compliance with design specifications
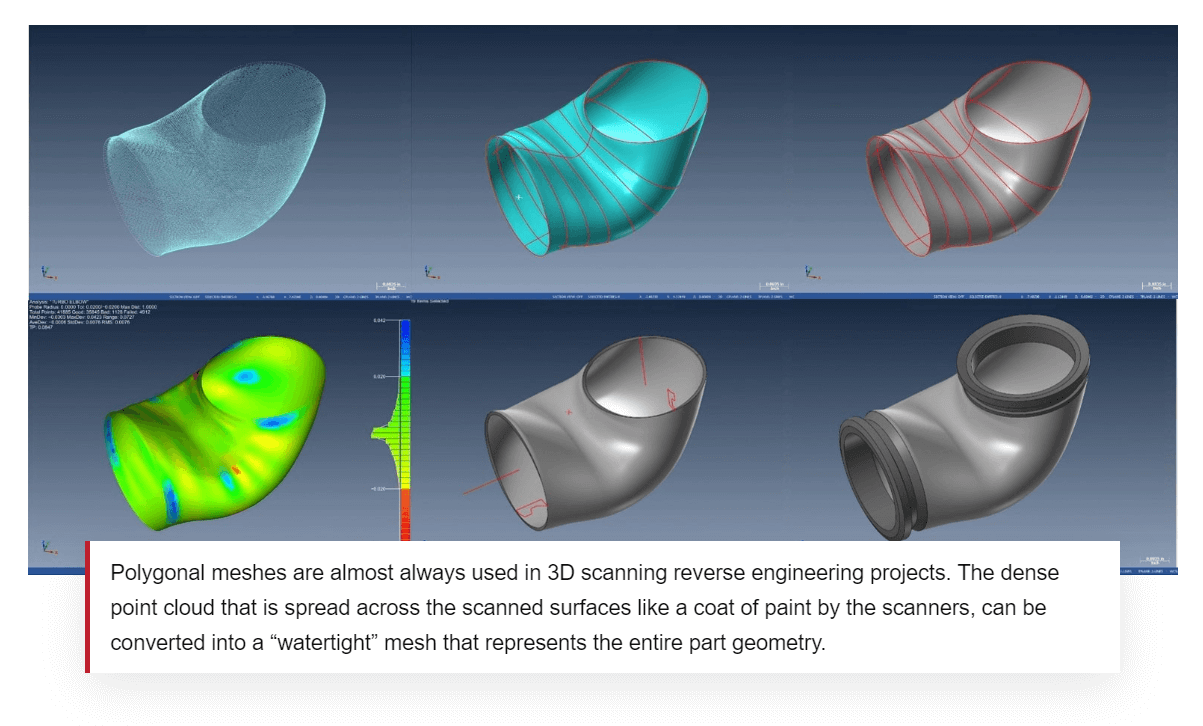
2. Automotive & Aerospace
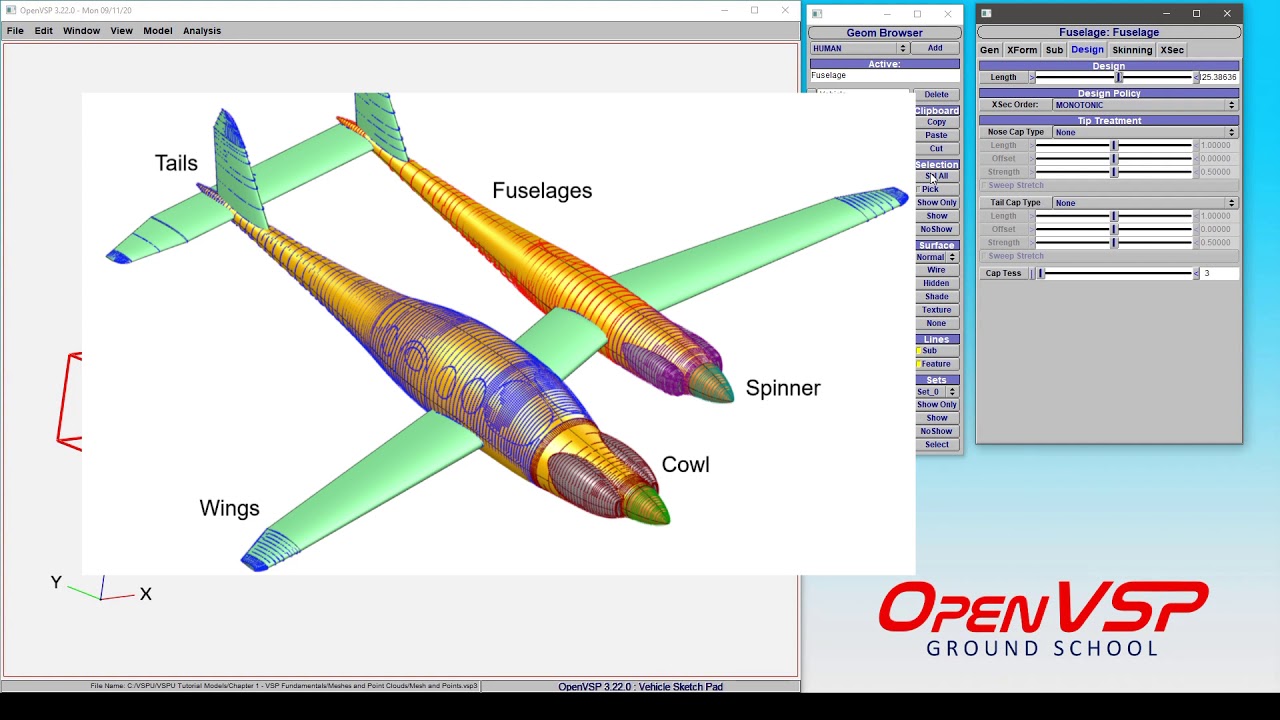
- Wear and deformation analysis of in-service parts
- Aerodynamic optimization through surface data
- Reverse engineering of legacy or damaged parts
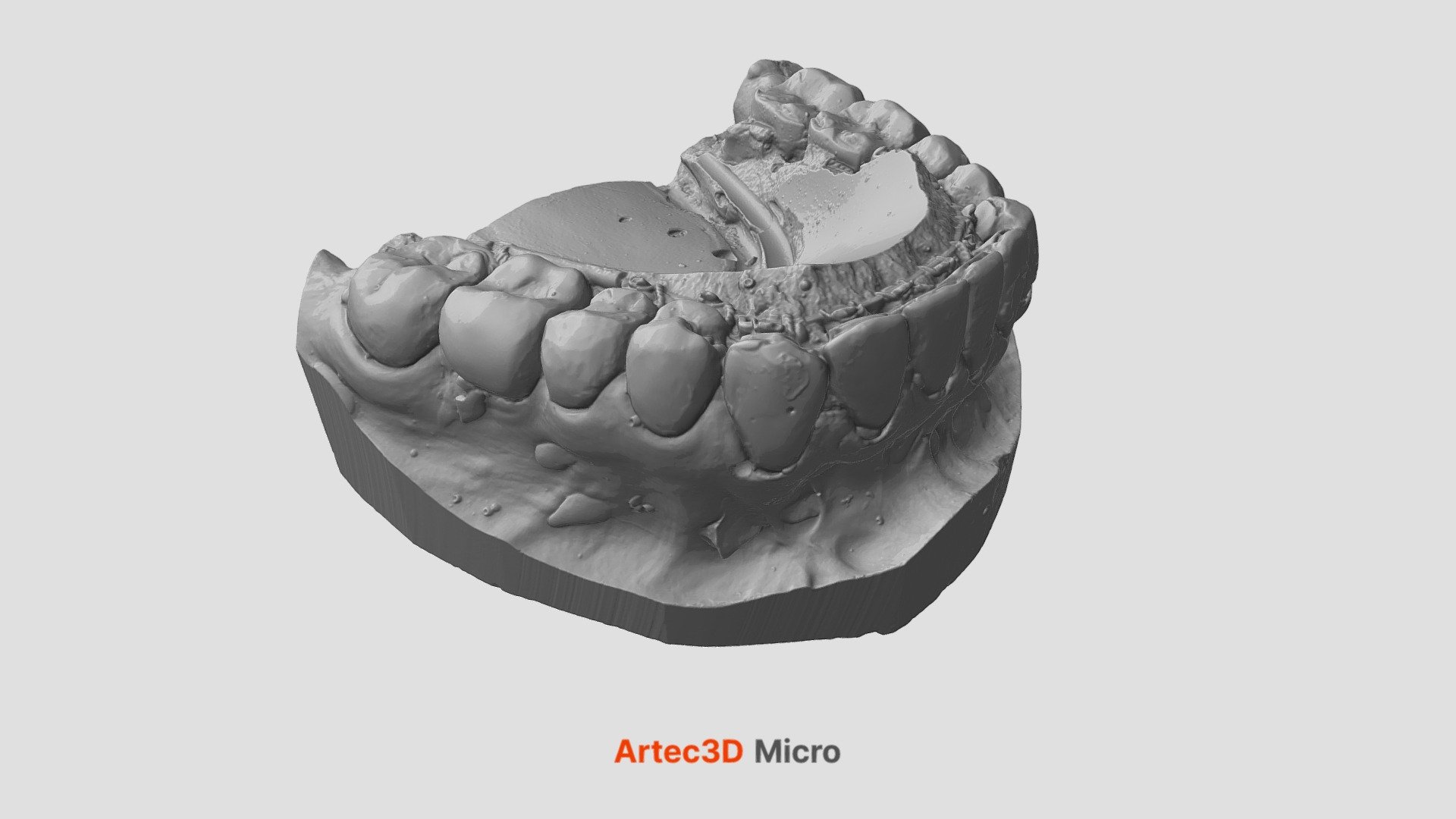
3. Healthcare & Medical Devices
- Improved patient comfort and fit
- Reduced manual molding and adjustments
- Faster production of custom devices
- Better clinical outcomes
4. Architecture & Construction
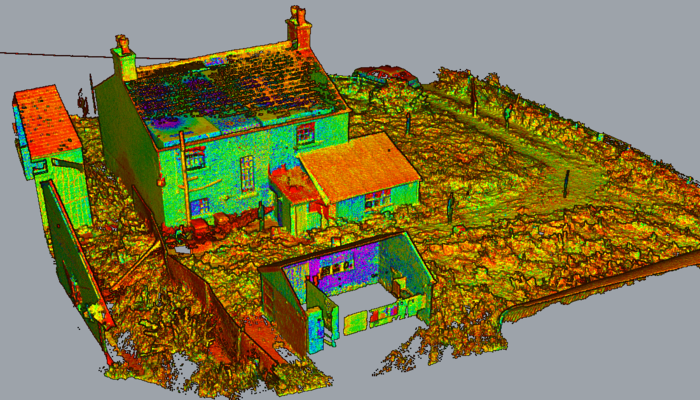
- Renovation and retrofit planning
- Structural analysis and clash detection
- Digital documentation of heritage buildings
- BIM model creation from scan data
Why 3D Scanning Matters
3D scanning fundamentally improves how industries capture and use real-world data. By replacing slow, manual measurement methods with fast, high-resolution scanning, organizations gain better accuracy, reduced errors, and greater confidence in decision-making.
Key Advantages
- Faster data capture
- Higher measurement accuracy
- Reduced human error
- Better design and inspection confidence
✨ In today’s competitive landscape, 3D scanning is not just a tool—it’s a strategic advantage.